Lithium ion Battery Won't Charge - 3 Revival Steps & Guide

Lithium ion batteries are a popular and reliable power source used in many consumer electronics and electrical devices. They offer users the convenience of longer-lasting, more powerful energy storage than other types of rechargeable batteries. Unfortunately, lithium ion battery charging problems can occur unexpectedly due to various factors. This article will discuss potential causes for why your lithium ion battery won't charge, as well as how you can troubleshoot and potentially resolve the issue.
The most common reason for lithium ion batteries not charging is that they have reached their end-of-life cycle or are damaged beyond repair due to overcharging or incorrect usage. Other potential issues include poor connections between the battery pack and charger, faulty chargers or adapters, depleted cells within the battery pack, internal short circuits, temperature extremes, and corrosion on the contacts.
In order to determine exactly what may be causing your lithium ion battery to fail to charge correctly, it is important that you understand all of these possible scenarios so that you can properly diagnose the problem at hand. The following sections will provide an overview of each scenario along with tips on how to identify them and troubleshoot accordingly.
Why the Lithium ion Battery Won’t Charge?
(1) The charging system is damaged
The underlying cause of a lithium-ion battery not charging can also be the failure of its associated charging system. When this occurs, it can have an array of far-reaching effects that could significantly damage both the power source and any device connected to it.
In order to understand why these issues occur, we must first consider how the lithium-ion battery works:
- Charge cycle: A charge cycle is when a battery goes through one full process from being fully charged to empty and then back up again. During each cycle, electrons are exchanged between the cells in order to maintain optimal levels.
- Charging systems: Charging systems are responsible for controlling voltage and current during recharging periods. The amount of charge sent into the cell determines how fast or slow it will recharge as well as how long it will last before needing another cycle.
A damaged charging system would prevent proper voltage regulation leading to overcharging which could result in permanent damage to the battery's internal components. Additionally, if too much current is allowed into the battery, it may cause excessive heating due to increased resistance in the cell walls resulting in further degradation of its performance capacity. This can ultimately lead to reduced lifespan and even complete failure of the entire unit. Therefore, ensuring your devices' charging system is working properly should always be done with caution and care.
(2) The charger is faulty
A lithium-ion battery is like a machine - it needs the right tools and parts in order to work correctly. It requires an appropriate charger that can provide sufficient voltage and current for charging. When this is not accomplished, then the battery will not charge properly or at all.
The most common reason why a lithium ion battery may be failing to charge is due to a faulty charger. Chargers are complex pieces of equipment with many components that need to interact correctly in order for them to function optimally. If any one of these elements fails, then it could lead to the battery being unable to receive power and thus remain unchanged. Furthermore, if the output from the charger does not match up with what the particular type of lithium-ion battery needs, then again it will fail to charge properly.
In general, there are two main points to consider when diagnosing a faulty charger: its power supply capabilities as well as its compatibility with the specific kind of lithium-ion battery used. To ensure optimal performance, both must be checked before troubleshooting further.
(3) Battery BMS system failure

A lithium-ion battery will not charge if the Battery Management System (BMS) has failed. The BMS is an integrated circuit that monitors and controls the charging process of a lithium-ion battery. It regulates the voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge to ensure safe operation. When it fails, the battery no longer charges properly or at all.
Common causes for a BMS failure include electrical short circuits due to foreign objects such as dust particles and liquid entering into contact with the internal components of the battery; incorrect wiring resulting in excessive current draw during charging; overcharging which can cause thermal runaway leading to damage to the cells; and aging due to repeated cycles without proper balancing causing deterioration of cell capacity and balance between cells. Additionally, some manufacturers have been known to use low-quality materials resulting in early failure of their battery's BMS systems.
Diagnosing a BMS issue requires specialized tools and knowledge along with experience working on these types of batteries. If left unchecked, a faulty BMS can lead to more serious issues like permanent damage or even fire hazards. Therefore repairing or replacing it should be done by qualified personnel only who are trained in safely handling lithium ion batteries.
(4) The battery is exhausted
A lithium-ion battery is a type of rechargeable energy storage device. It contains two electrodes, an anode and a cathode, that store charge when the battery is charged up. The reason why a lithium-ion battery may not be charging can be attributed to the fact that it has exhausted its stored charge and needs recharging in order to function properly again.
The exhaustion of a lithium-ion battery's stored charge occurs due to several factors such as overuse, age and improper charging techniques. Overuse refers to using the battery for extended periods of time without allowing it to rest in between uses; this causes the battery’s capacity level to decrease gradually until it reaches zero and eventually stops working altogether.

Age also plays a role in reducing the amount of energy stored by the battery; with time, cells inside the battery begin to corrode or leak electrons, thus lowering their ability to hold charge effectively. Lastly, improper charging techniques such as overcharging or undercharging can damage internal components within the battery and cause them to become nonfunctional too quickly.
In order for a Li-ion battery to remain functional, regular maintenance should be performed to avoid battery failure, such as periodic discharge followed by recharging or replacement of worn parts when necessary. In addition, users should develop proper charging habits, including avoiding leaving the battery plugged in overnight or constantly replenishing the existing charge, rather than completely draining it every time it is used and then recharging it from the beginning.
How to fix a Lithium ion Battery Won't Charge?
Lithium batteries are ubiquitous in our daily lives, powering everything from smartphones to electric cars. But what should you do when your lithium battery won't hold a charge? Don't despair, there are a few steps you can take to fix your battery and get it working again.
(1) Reactivate the battery
The following steps can usually be taken to reactivate the battery and get it working again. Let's take a 3.6V Li-ion battery as an example.
- Put the battery in the charger - First, place the battery in the charger, and let it sit for at least 10 minutes. This will allow the battery to warm up slightly, and sometimes, the battery needs a small amount of charge to activate it.
- Check the voltage - Use a multimeter to check the voltage of the battery. If the voltage is below the minimum required for charging, which is typically around 2.5V, use a compatible power supply to give the battery a small boost of power. Connect the battery to a power supply that is rated for the same voltage as the battery, and set the current to a low value, such as 50mA. Charge the battery for 10-15 minutes, then measure the voltage again. If the voltage has increased, place the battery back in the charger and attempt to charge it as normal.
- Try a different charger - If the battery still doesn't charge, try a different charger. Make sure that the charger is compatible with the battery, and that the voltage and current ratings are appropriate.
- Charge in pulses - In some cases, charging the battery in pulses (short charging periods with intervals of rest) can help to reactivate it. Use a charger that has a pulse charging mode, and charge the battery for 10-15 minutes at a time, with breaks of 5-10 minutes in between. Repeat this process several times, and check the battery voltage periodically.
- Store the battery at room temperature - If the battery has been stored in a cold environment, it may need to be brought to room temperature before it can be charged. Store the battery in a warm room for several hours before attempting to charge it.
(2) Repair your battery
If the steps above don't work, it's time to move on to repairing the battery. Check the battery for physical damage or corrosion - if so, damaged parts will need to be replaced. If the battery is still intact, try wiping the contacts with a soft cloth and rubbing alcohol. Sometimes dirty contacts can prevent the battery from charging properly.
(3) Replace the battery
If it is still unable to continue charging, it is likely that the service life of the lithium battery has reached its limit, including the high temperature of the battery, the loss of the ability to maintain a charge, and excessive loss of battery life, etc., which will lead to premature failure of the battery.
Finally, if none of the above steps work, the battery may be permanently damaged and will need to be replaced. Remember to handle lithium batteries with care and always follow the manufacturer's instructions when charging or storing them.
How Can I Tell If A Lithium Battery is Dead?

The life cycle of a lithium ion battery is finite, and it must be replaced after its charge has been expended. Understanding how to determine when the battery's capacity for holding a charge has reached its limits can help you make an informed decision about replacing it.
To tell if your lithium-ion battery is dead, start by checking the voltage with a multimeter. If the reading shows less than 2.7V, then there is most likely no remaining energy in the cell and it should be discarded or recycled properly. Additionally, observe any changes in physical characteristics such as bulging cases or leakage; these are often indicators that the battery has failed and needs to be removed from service immediately. It is also recommended to test your device after each use to ensure that all cells are operating at their optimal level.
If none of these methods yield satisfactory results, take your device to an experienced technician who can inspect it further for signs of damage or failure. By taking proactive steps like these, you can prevent potential safety hazards associated with using defective batteries in everyday devices.
What Happens When A Lithium Battery Dies?
When a lithium ion battery dies, it can no longer be recharged. This is because the chemical composition of the electrolytes in the cells has become so depleted that they cannot accept or store electricity any longer. The depletion of these chemicals is caused by overcharging and excessive heat exposure which cause irreversible damage to the cell's structure.
A dead lithium-ion battery will not charge up again even if it has been left unused for a while. It must be disposed of correctly as it contains hazardous materials such as cobalt, nickel, lead and acid electrolyte. Disposing of them incorrectly can pose risks to people and the environment due to their flammable nature and potential contamination of drinking water sources. Furthermore, recycling should always take precedence when disposing of old batteries as this helps conserve resources and prevent further pollution from mining new raw materials used in their manufacturing process.
What Will Happen If the Lithium ion is Not Charged?

Lithium-ion batteries are an essential part of many electronic products, providing a reliable and easily rechargeable power source. However, if these batteries are not recharged regularly, their lifespan will be shortened.
Even when not in use, lithium-ion batteries have a self-discharge rate of 5% per month,
If you don't recharge your Li-Ion battery regularly, it will eventually die completely and won't be able to provide you with power until the battery is replaced.
To ensure your lithium-ion batteries remain useful for as long as possible, be sure to charge them regularly and always store them in a cool place away from extreme heat or cold.
How Long Can A Lithium Battery Last Without Charging?
The lithium ion battery is a marvel of modern technology. Its capacity to store energy in a lightweight and compact form has revolutionized the way we interact with our environment. But like all batteries, it needs to be recharged from time to time to maintain its efficiency and prevent damage. So how long can a lithium battery last without charging?
To answer this question, one must consider several factors such as temperature, discharge rate, storage conditions and initial state of charge (SOC). In general, at room temperature and moderate discharge rates, a fully charged Li-Ion cell will have approximately 500 full-depth cycles or 1 year of service life before reaching 80% capacity loss. This means that if you are using your device regularly and keeping it properly maintained, you should expect to get around two years' use out of your Li-Ion battery before needing to replace it.
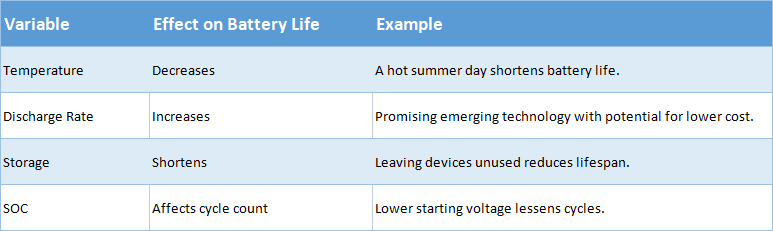
However, these estimates may not always hold true due to variations in usage habits, environmental conditions, and other factors which could affect overall performance. For example, high temperatures reduce the available capacity while leaving the device idle for extended periods can cause irreversible degradation over time even when no current is drawn.
Therefore proper maintenance is important for ensuring optimal performance throughout the service life of the battery. With regular inspection, timely replacement, and careful management of usage patterns and external influences you can maximize the lifespan of your Li-Ion cell.
How Long Does it Take to Charge a Dead Li-ion Battery?
When charging a dead lithium ion battery, the time required depends on several factors.
Typically, it can take 2 to 3 hours for a lithium ion battery to go from fully drained to fully charged, faster charge times can be achieved with more advanced chargers.
Actual times will vary depending on the age and condition of the battery and the capacity and current rating of the charger.
Charging the battery only when necessary and not leaving it connected for long periods of time is essential for proper battery maintenance. This will reduce the chance of overcharging or discharging wear and ensure your lithium ion battery continues to perform at its best.

How Many Times Can a Lithium ion Battery be Charged?
Lithium-ion (Li-Ion) batteries are becoming increasingly popular due to their low maintenance and long cycle life. When lithium-ion batteries are properly charged and discharged with the correct charger, they can cycle hundreds of times before losing capacity.
It is very important to keep the charge level between 20% and 80%, and avoiding a full discharge of more than 100% will help ensure longer lithium ion battery life and more recharge cycles.
Depending on the manufacturer of a lithium ion battery and the type of cells it contains, its charge cycle can vary from 500 to over 10,000 cycles.
HARVEYPOW lifepo4 batteries can cycle at least 8000 times, and the service life is as long as 20 years.
Are Dead Lithium ion Batteries Safe?
Lithium-ion batteries are gaining popularity due to their excellent performance and long service life, but
At the end of its useful life it may be hazardous and must be disposed of properly.
It is important to note that lithium-ion batteries may still contain a charge even after they are depleted. This means that mishandling of any lithium battery must always be avoided as it may cause an explosion or fire.
Additionally, lithium recycling should only be performed by experienced professionals, as lithium batteries pose serious risks if not recycled properly. Lithium-ion batteries can be disposed of safely and without worry if care is taken.

How Do I Know If My Li-ion Battery is Damaged?
It is very important to check your lithium ion battery regularly for signs of damage.
First check the appearance of the battery for bulging, swelling or shrinking, irregular shape compared to new, and terminal corrosion.
If any of these signs are present, avoid using the battery and opt for a replacement instead. Otherwise, you run the risk of your lithium ion battery failing to charge or worse - catching fire due to overcharging.
Next check its performance by observing how quickly it discharges, how long it takes to fully charge, and what its current capacity is.
Taking comprehensive precautions will help ensure that your lithium-ion battery will remain safe and working for a long time.
What Are The High-Risk Signs Of Lithium-Ion Batteries?
When it comes to lithium-ion batteries, understanding the warning signs of potential problems is critical in order to prevent any damage or injury. Lithium ion batteries can be hazardous when mishandled and should always be treated with caution. Some of the high-risk signs associated with lithium-ion batteries include swelling, discoloration, leaking electrolytes, and a decrease in charging capacity.
Swelling is one of the most common issues that occur with Li-Ion batteries due to overcharging or overheating. As the battery swells up from an internal pressure buildup, it indicates a potentially dangerous state where the cell could rupture or even catch fire if not addressed immediately. The discoloration is another indication that something isn’t right; for example, yellowish spots may indicate corrosion on the cells caused by leakage of electrolytes within them. Leaking electrolytes are also a sign of danger as they can cause short circuits in other components connected to the battery packs. Lastly, a decrease in charging capacity might suggest the aging of individual cells which have lost their ability to store enough energy anymore.
These are only some of the risks related to operating lithium ion batteries and users must take extra care while handling them so as not to interfere with their safety features and protocols put into place by manufacturers. It’s important to stay informed about all aspects of these powerful storage devices and make sure you use proper precautions whenever working with them. By taking some simple steps such as monitoring your device for unusual changes in temperature or physical appearance, you can avoid many unnecessary hazards associated with using Li-Ion technology safely and efficiently.
Summarize
Lithium-ion batteries are an integral part of our daily lives and a key factor in the advancement of technology. However, they can be prone to certain issues that prevent them from charging properly. This article has explored some common causes of this issue such as faulty chargers, battery management system failure, damage to the charging system, or simply exhaustion of the battery itself.
Furthermore, solutions were provided on how to fix Li-Ion batteries that won't charge, whether it is possible to revive dead lithium-ion batteries, how many times a lithium-ion battery can be charged and how to test battery performance. Lastly, high-risk signs of lithium-ion batteries were discussed which included swelling or bulging of the casing around the cells and release of noxious gasses during usage.
It is important for consumers to understand these risks associated with lithium ion batteries so they can make informed decisions when purchasing them and ensure their safety when using them. Proper maintenance should also be taken into account in order to prolong its life span and avoid unexpected failures due to improper use or storage conditions. Taking all these factors into consideration will help protect both users and manufacturers alike from any potential harm caused by malfunctioning lithium ion batteries.
Choose the Best Lithium Battery
HARVEYPOW lifepo4 battery manufacturer is paving the way for green energy development, with our superior solar batteries offering up to 8,500 cycles and 90% depth of discharge.
Our experienced technical teams can also customize unique solutions tailored to your needs – plus offer OEM/ODM services so you have a product that's truly one-of-a-kind!
More FAQs
(1) Will a trickle charger charge a dead lithium battery?
Yes, the trickle charger is designed with low-rate charging in mind, and the weak current of trickle charging can be used to "precharge" the battery. After the voltage rises to the normal range, the current can be increased to continue charging.
(2) Will the battery fail to charge because it's dead?
It needs to be analyzed according to different situations:
- Capacity: Lithium-ion batteries gradually lose capacity over time and use until they can no longer be charged.
- Voltage: If the voltage level of the battery falls below a certain threshold, it affects its ability to accept a charge, which can be resumed again by activation.
- Age: If the age of the battery is unknown or has exceeded its maximum rated cycle number, it may not be able to accept a full charge again without risk of damage or failure.
- Condition: Excessive heat, vibration, physical shock, or chemical exposure can cause permanent damage to the cells inside the battery, which will prevent them from fully charging again, regardless of their age or condition.
(3) What causes a battery to explode?
- Overcharging - When the charger continues to provide power after the battery is full capacity, this can cause overheating and, in extreme cases, explosion of the battery.
- Internal Short Circuits - As cells within a battery pack wear and tear, components inside the cells may come into contact, creating an electrical connection between them, bypassing normal electrical circuits and increasing heat generation.
- Mishandling of the battery - for example a lithium-ion battery that is accidentally punctured or damaged may spark or catch fire due to its highly flammable electrolyte solution. Additionally, storing batteries near flammable materials such as paper or cloth further exacerbates this danger, as any spark can quickly travel to nearby objects, causing disaster.
(4) Will putting the lithium battery in the fridge charge it?
Rapid cooling in the refrigerator can cause condensation to form on the outer surface of the battery, which increases corrosion and power loss over time. Instead, it is recommended that these batteries be stored or used at room temperature for optimal performance.
Learn More Top Questions About Lithium Batteries!
