秘密の発見: Lifepo4 バッテリーはどのように作られるのか?

リン酸鉄リチウム (LiFePO4) バッテリーは、エネルギー密度が高く自己放電率が低いことから、ますます人気が高まっている充電式バッテリーの一種です。家庭用電化製品から電気自動車まで、さまざまな用途に使用されています。この記事では、LiFePO4 バッテリーの製造方法、その製造に関係する材料やプロセスについて詳しく説明します。
の LiFePO4電池の製造工程 製造には、原材料の混合、電極の形成、セルの組み立て、最終製品へのカプセル化など、いくつかのステップが含まれます。製造で最も重要な部分は、組み立て前にコンポーネントの品質が良好であることを確認することです。コンポーネントが安全要件を満たしていることを確認するには、プロセス全体を通じて複数回テストする必要があります。
作る LiFePO4電池 高性能で信頼性の高い製品を製造するには、製造工程の各段階で細心の注意を払う必要があります。特に、材料の選択やさまざまな部品の温度管理には特別な注意が必要です。これらの要素は、製品の最終的な性能を決定する上で重要な役割を果たします。 LiFePO4バッテリー 生産により、メーカーは最適な性能特性を備えた信頼性の高い製品を生産できます。
意味
リン酸リチウム(LiFePO4)電池 高いエネルギー密度、長いサイクル寿命、低コストのため、近年人気が高まっている充電式バッテリーの一種です。
LiFePO4 セルは、電気自動車からノートパソコンや携帯電話などの家電製品まで、さまざまな用途に使用されています。LiFePO4 セルの製造には、原材料の選択から始まり、完成したバッテリー パックの組み立てまで、いくつかのステップが含まれます。
作成の最初のステップ LiFePO4バッテリー 適切な原材料を選択することです。原材料には、リチウム金属酸化物、グラファイトアノード材料、電解液、セパレータ膜、集電体が含まれます。最終製品が安全基準を満たし、最適な性能を発揮するように、各コンポーネントを慎重に選択する必要があります。
コンポーネントが選択されると、セルまたはパックに組み立てる前に、それぞれの要件に従って処理する必要があります。これには通常、粉末を混合し、電極を活性物質でコーティングし、電極を特定の形状に成形し、電解質溶液を充填し、真空状態で密封することが含まれます。
このプロセスが完了すると、各セルはより大きなセルに組み込まれる前に、すべての仕様を満たしていることを確認するためにテストされます。 パックまたはモジュール より高い出力を必要とするアプリケーションで使用します。
#1 Lifepo4 細胞生産
生産1:原材料の準備
正極はリン酸鉄リチウム (LiFePO4) で作られ、負極はグラファイトまたはその他の炭素質材料で作られ、その間のセパレーターはポリエチレンやポリプロピレンなどのポリマーで作られ、電解質はエチレンカーボネートやジメチルカーボネートなどの有機溶媒に溶解した塩で構成されています。これらの部品はすべて、セルに組み立てる前に欠陥がないか慎重に検査されます。1 つのミスが、将来的に壊滅的な故障につながる可能性があります。
生産工程2:正極製造
正極は、活物質、導電剤、バインダーの 3 つの部分で構成されています。これらのコンポーネントを作成するには、次の操作を行います。
- まず、リン酸鉄リチウム(LFP)粉末やグラファイトなどの活性物質を作成する必要があります。これは、鉱物を小さな粒子に粉砕し、それをさまざまな化学物質と混合して、バッテリーでの使用に適したものにすることで行われます。
- セル間の電子の流れを促進するために、カーボンブラックなどの導電性物質を追加する必要があります。
- 最後に、電池に使用する形状に成形する際にすべての材料がくっつくように結合剤を使用する必要があります。
得られた混合物は、製造工程で接着剤があらかじめ塗布された薄いアルミホイルシートに塗布され、バッテリーの組み立てに必要になるまで保管されます。
正極は可燃性が高いため、取り扱いには注意が必要です。職場環境で定められた安全規則や防火・保護方法に関するベストプラクティスに従って取り扱う必要があります。
生産工程3:負極製造
調査によると、全世界の約90% lifepo4バッテリーセルは電力を供給されます グラファイト製の負極によって実現されます。この材料は軽量でコスト効率に優れ、優れた導電性媒体を提供します。
- グラファイト粒子はナノメートルサイズに切断され、ポリフッ化ビニリデン (PVDF) などのバインダー材料と混合され、バッテリー構造全体に均一に分散されます。
- これらの粉末粒子は、「カレンダー」と呼ばれる特殊な機械を使用して圧縮されます。この圧縮プロセス中に、熱と圧力が組み合わさって、設計仕様に合わせた形状の固体グラファイトシートが形成されます。
- 完成すると、このシートは負極アセンブリになります 各LifePo4バッテリー内部.
長期にわたって最適なパフォーマンスを確保するには、製造のあらゆる段階で品質管理措置を講じる必要があります。これには、粒度分布、水分レベル、および製造精度に必要なその他のパラメータの慎重な監視が含まれます。
生産4: カソードとアノードの組み立て
まず、電極を組み立てる準備をする必要があります。混合プロセスでは、カーボン ブラック粉末とグラファイトまたは人造グラファイト粉末をアセチレン ブラックなどの導電剤と混合し、次にポリフッ化ビニリデン (PVDF) 溶液などのバインダー溶液を加えて均一な混合物を作ります。この混合物は、バッテリー セルの正極と負極の両方の電極材料になります。
これが完了したら、カソードとアノードをそれぞれの構造に組み立てます。
カソードアセンブリ:
- セパレータシートは、高温の圧力ローラーを使用して積層された 2 層の電極材料の間に置かれます。
- ラミネートの各側面にコネクタが取り付けられており、バッテリー パック内の他の部品に接続できます。
- 最後に、ニッケルメッキ銅タブを接続してカソードアセンブリを完成させます。
アノードアセンブリ:
- 陽極も 2 つの層で構成されていますが、それらを積層するのではなく、単に重ねて手で所定の位置に押し付けます。
- ニッケルコーティングされたスチールコネクタをスタックの両側に追加し、その同じコネクタにニッケルタブをはんだ付けしてアノードアセンブリを完成させます。
バッテリーの設計に応じて、電極は交互に配置され、円筒形または角柱形に巻かれます。巻線は、材料が適切に整列し、均等に分散されるように慎重に制御されます。その後、最終的に、使用可能な完成したバッテリーセルハウジングユニット内にまとめられます。
製造工程5:電解液充填
次の製造段階は、電解質を充填することです。エチレンカーボネート、ジメチルカーボネート、および六フッ化リン酸リチウムの組み合わせが、注入ポートからセルに追加されます。この混合物により、電圧が電極に印加されたときに、電極間に電流が流れます。混合物をセルに注入した後は、動作中に物質が漏れたり入ったりしないように密閉する必要があります。
製造6: Lifepo4セルのシーリング
LifePo4 セル製造プロセスの最後のステップは、シーリングです。この手順では、シーラント材を使用してセルを気密に密閉し、電解質の汚染や漏れを防ぎます。シーリングは、圧縮溶接、ホットメルト接着剤の塗布、超音波接合、レーザー溶接、熱かしめなど、さまざまな技術を使用して行うことができます。
| 方法 | 利点 | 不利益 |
|---|---|---|
| 圧縮溶接 | 耐久性のあるシール 処理時間が速い 低コストの材料が必要 | 高温が必要 設計の柔軟性が限られている |
| ホットメルト接着剤の塗布 | 柔軟な設計 耐熱性 非常に低いエネルギー入力 | 機械的強度が低い 長い硬化時間 |
| 超音波接合 | 生産速度が速い 複数の層を同時に接着可能 優れた構造的完全性と電気絶縁性 | より高価な機器が必要 大型部品には適していません |
| レーザー溶接 | 部品表面との接触なし 溶接サイズと形状の正確な制御 他の方法よりもコンポーネントへの負担が少ない | 高価な機器が必要 機械設定の複雑なプログラミングが必要 |
| ヒートステーキング | 自動化組立ラインへの容易な統合 接合工程中の部品表面の変形が最小限 成形作業完了後の取り扱いがほとんど不要 | 時間のかかるセットアップ手順 |
生産6: セルシールテスト
密封後に実施されるテストには、漏れの有無の確認と損傷の兆候の目視検査が含まれます。漏れテストでは、バッテリーが入っているケースに圧力をかけ、圧力がかかった表面のどの部分からでもガスが漏れていないかを調べます。目視検査は、密封プロセスの不備や、製造上の欠陥や取り扱いミスなどの外力によってケースの両側に変形がないかを確認するために使用されます。
#2 Lifepo4 バッテリーパックアセンブリ
の lifepo4 バッテリーパック 組み立ては、生命そのものの複雑な仕組みを象徴する複雑なプロセスです。組み立ては個々のセルから始まります。各セルは細心の注意を払って製造され、品質保証のためにテストされます。次に、これらのセルを直列または並列に接続して、使用目的に基づいて特定の電圧要件を持つより大きなモジュールを組み立てます。
次に、水、ほこり、極端な温度などの外部要素からモジュールを保護するための筐体を設計する必要があります。この筐体は、必要な保護レベルに応じて、単純なプラスチック シェルから金属ケースまでさまざまです。筐体の内部レイアウトも、すべての電気接続が安全で、動作中に発生する熱の蓄積が最小限になるように、慎重に計画する必要があります。これが完了すると、回路基板、配線ハーネス、コネクタなどのコンポーネントを顧客の仕様に従って追加できます。最後に、最終テストが行われ、バッテリー パックが出荷準備完了になる前に、絶縁材やヒューズなどの追加の安全機能を含める場合があります。
ステップ1: 外部評価
組み立て工程の最初のステップは LiFePO4バッテリー 各セルに目に見える損傷がないか検査することです。この検査には、ケースにへこみ、傷、または跡がないかのチェック、およびすべてのコンポーネントが存在し、しっかりと固定されているかどうかの確認が含まれます。検査員は、端子に腐食がなく、接点がきれいであることも確認する必要があります。さらに、金属構造の変色や酸化の兆候にも注意する必要があります。
この段階では、セル間のショートや緩い接続など、安全上の問題や性能効率の低下につながる可能性のある異常がないか確認することが重要です。これらの問題が特定されると、次の組み立て手順に進む前に対処できます。組み立て前に各セルを検査することで、メーカーは高品質のバッテリーのみが製造されることを保証できます。
ステップ2: 容量、内部抵抗、電圧を測定する
パフォーマンスの主な鍵は ライフポ4 バッテリーパックはバッテリーセルの一貫性です。そのため、組み立てる前に、各バッテリーの容量、内部抵抗、電圧を測定する必要があります。一定の生産基準の差に応じて、グループに分けられてから組み立てられます。差が小さいほど、性能は優れています。
このプロセスは、バッテリーをテストシステムに接続して、開放電圧(OCV)、短絡電流(SCC)、インピーダンスなどの電気的パラメータを測定することから始まります。OCVはフル充電時に測定され、SCCの読み取りは充電完了後に行われます。 バッテリーが放電しました 0ボルトまで。インピーダンス測定は、電流または電圧で接続された2つの端子間にどれだけの抵抗が存在するかを決定します。これらのパラメータは、各端子の全体的な品質とパフォーマンスに関する貴重な洞察を提供します。 LifePo4バッテリー パックに組み立てる前。
ステップ3: モジュールを直列に接続する
各単一 LifePo4 セルの電圧は 3/3.2V であり、直列接続によって電圧が増加し、顧客の要求パラメータを満たします。
そのため、まずは複数の lifepo4セルは、自動パレタイジング、プレス、空気圧パレタイジング、レーザー溶接などの方法を通じて、lifepo4バッテリーが パックは激しい揺れがあっても安定した構造を保つことができ、緩みにくいです。また、手作業による溶接と比較して、レーザー溶接はより効率的で、より安定しており、溶接誤差も小さくなります。
ステップ4: モジュールをハウジングに挿入する
- モジュールのコンポーネントに欠陥や不完全な点がないか確認します。
- 必要に応じて、すべての部品が適切にフィットするように調整してください。
- すべてをチェックして正しいことが確認できたら、モジュールをケース内に正確に配置し、しっかりとネジで固定します。
上記の手順により、輸送中および使用中にデバイス全体がしっかりと固定され、振動や衝撃による損傷が防止されます。潜在的な問題をさらに減らすために、ハウジングの端の周囲に必要に応じて追加のシールを取り付けて、ほこりや湿気の侵入などの環境要素からさらに保護することもできます。
ステップ5: 電圧サンプリングラインの設置
このステップは、外部デバイスまたは回路がバッテリーの動作電圧を測定できるようにすることです。
- まず、この手順では絶縁電線を適切な長さに切断する必要があります。
- 次に、むき出しの端をそれぞれ正極と負極の端子に接続します。この操作中に短絡が発生しないことを確認します。
- 各ワイヤのもう一方の端をマイクロコントローラ ボード上のアナログ-デジタル コンバータ (ADC) ポートに接続するか、または集積回路 (IC) に直接接続します。
この接続が確立されると、どの監視システムでもパフォーマンスに悪影響を与えることなく、電圧を正確にサンプリングできます。一貫した読み取り値を確保するには、すべての接続が安全で適切に絶縁され、感電や漏電などの潜在的な危険を防ぐことが重要です。
ステップ6: 配線ハーネスの配置
この段階では、すべてのコンポーネントがテストされ、それぞれの PCB に組み立てられます。専門のエンジニア チームが各ワイヤを適切な端子に接続する前に、損傷や異常の兆候がないか慎重に検査します。
ハーネスは、バッテリーが生産ラインに積み上げられるときに互いに干渉しないように位置合わせする必要があります。緩んだ撚り線や誤った接続があれば、すぐに修正する必要があります。そうしないと、大幅な遅延が発生する可能性があります。すべてのケーブルは保護絶縁材で覆われ、適切なラベルが付けられるため、技術者はメンテナンスやトラブルシューティング作業中にどのワイヤーがどこに接続されているかを簡単に識別できます。
すべての仕上げ作業が完了したら、次の生産段階に進む前に、各ユニットに欠陥がないか再度チェックされます。
ステップ7: BMSのインストール
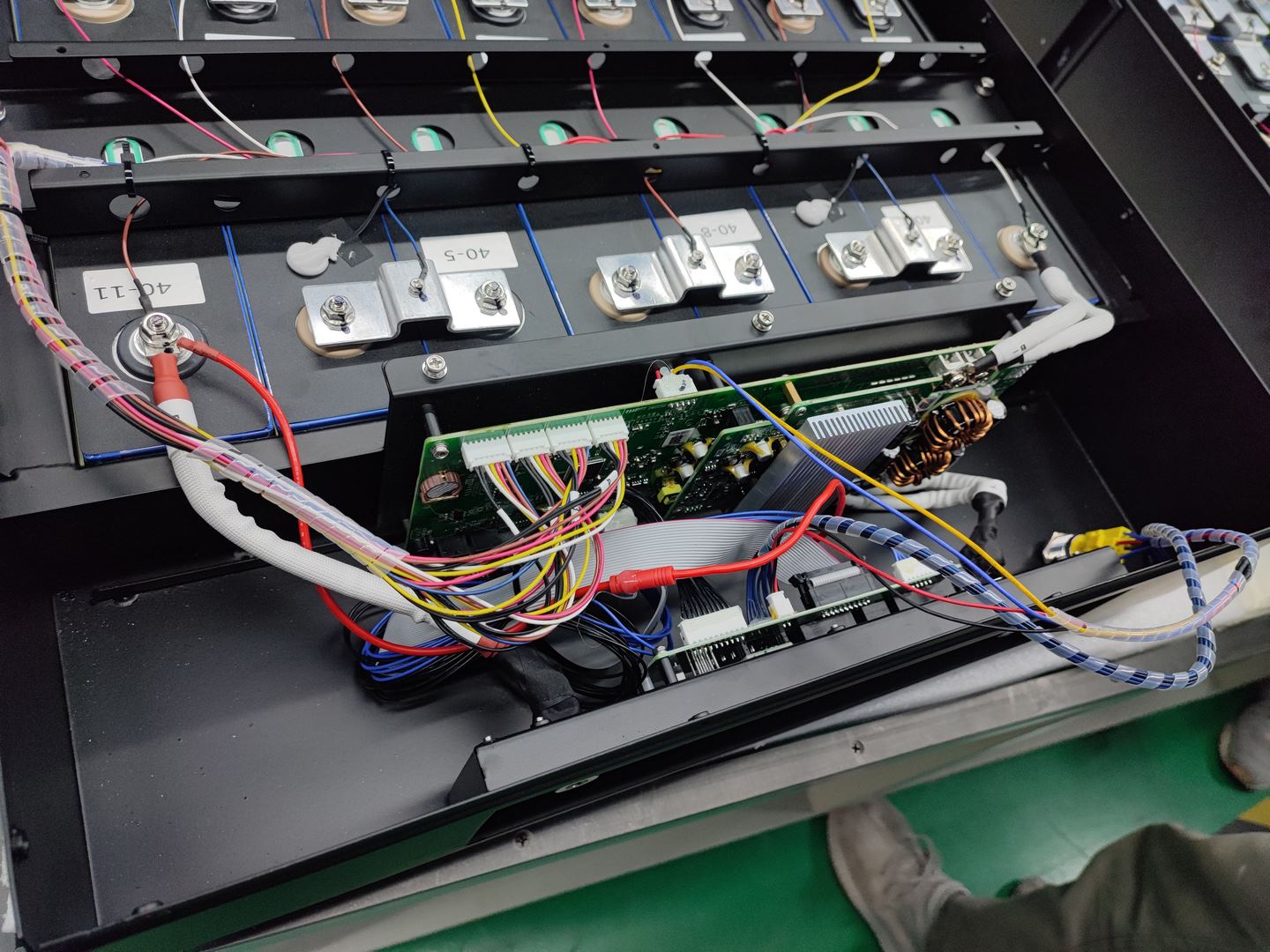

組み立ての第7ステップ LiFePO4バッテリーはバッテリー管理システムのインストールです (BMS)。BMS は、大きなバッテリー パック内の個々のセルを監視および制御する電子回路です。これにより、バッテリーの最適なパフォーマンス、安全性、および寿命が確保されます。また、効率の低下やシステム全体の壊滅的な障害につながる可能性のあるセルの過充電や過放電も防止します。
BMS は、各セルにワイヤーで接続して設置します。配線ハーネスは、システム内のさまざまなコンポーネント間で干渉が発生しないように慎重に配線する必要があります。すべての接続が適切に行われると、BMS の電源が入り、自動的に監視機能を開始します。単一セルの過充電や過放電などの異常が発生した場合は、システムのプログラム方法に応じて適切な処置が講じられます。このようにして、バッテリーの正常な機能を長年にわたって確実に維持することができます。
ステップ8: バッテリーパックケースカバーの密封
「悪魔は細部に宿る」ということわざがあります。リチウムイオン バッテリー パックを組み立てる最後の組み立て手順では、ケース カバーを密閉して、すべてのコンポーネントがほこりや水などの外部要素から保護されるようにします。組み立て手順に関する重要なポイントは次のとおりです。
- ケースカバーを固定する前に、バッテリーパックのケースの端の周りにシーラントまたは接着剤を塗布する必要があります。
- 一部のモデルでは、湿気による損傷をさらに防ぐために熱収縮チューブも使用されることがあります。
- ケースカバーを取り付ける前に、露出しているすべての端子に防錆グリースを塗布する必要があります。
- 密封されたら、バッテリー パックの他の部分に接続するために、ワイヤーを指定された穴に通す必要があります。
- 最後に、組み立て工程が完了したら、シーリング工程中にエラーが発生していないことを確認するための検査が必要です。
この最後のステップは、バッテリー内の各セルが適切に絶縁され、安全に保たれ、寿命を通じて最適なパフォーマンスを維持できるようにします。リチウムイオンバッテリーを構築する際には、すべての予防措置を講じることで、ユーザーは安心して lifepo4バッテリーは安全かつ効率的であり続ける 時間とともに。
#3 テストと品質管理
バッテリーセルは複雑な機械であり、すべてのバッテリーは厳しい性能基準を満たす必要があります。品質管理は lifepo4 製造プロセスの不可欠な部分です。まず、組み立て前に個々のセルをテストし、基本的な基準を満たしていることを確認します。パックに組み立てられたら、製品全体に対してさらにテストが行われます。
品質管理の目的は 2 つあります。
- コンポーネントまたは構造上の欠陥を検出するため。
- 完成品が顧客の要件と業界の安全基準に準拠していることを確認します。
lifepo4バッテリーの最も重要なテストはサイクル寿命です。これは、バッテリーが問題なく充電/放電できるサイクル数です。 失敗 容量損失またはその他の損傷により、予定より早く故障する場合があります。
これらのテストを正確かつ客観的に実行するために、メーカーはサイクラーやインピーダンス アナライザーなどの自動化された機器を使用します。これらの機器は、内部抵抗、エネルギー密度、急速充電中の温度上昇、時間の経過に伴う自己放電率など、さまざまなパラメータを測定します。
生産段階の異なる複数のユニットの結果を比較することで、 メーカー 異常を素早く特定し、必要に応じて是正措置を講じることができます。
セルがこれらのテストのいずれかに合格しなかった場合は、そのセルは廃棄されるか、必要な基準をすべて満たすまで再加工される必要があります。すべてのテストに合格して初めて、バッテリーは、電源に信頼性の高いパフォーマンスを求める顧客向けに販売されます。
#4 梱包と配送
LiFePO4 セルが製造されると、梱包して目的地に発送する必要があります。梱包は、輸送中にセルが損傷したり汚染されたりしないようにするための製造プロセスの重要なステップです。出荷物のサイズに応じて、保護のためにさまざまな種類の梱包材が使用される場合があります。
少量の荷物の場合は、衝撃や振動から各セルを保護するために、フォームまたは気泡緩衝材で裏打ちされた個別の箱を使用できます。大量注文の場合は、安定性を高めるために、段ボールとストレッチフィルムを複数層使用する場合があります。
また、発送前に必要な配送ラベルがすべて正確に印刷され、各箱に貼り付けられていることも重要です。これには、送信者の住所、受信者の住所、パッケージの内容、重量などの基本情報が含まれている必要があります。
さらに、顧客から要求された特別な指示も、ラベルに直接記載するか、バーコード スキャン システム (使用可能な場合) を通じて記載する必要があります。これにより、税関でのラベルの誤記による遅延がなく、スムーズな配送が保証されます。
最後に、各パッケージに必要なラベルがすべて貼られたら、注文量と必要な移動距離に応じてパレットまたはトラックで出荷される前に品質管理チェックを受ける必要があります。ここでは、工場の敷地を離れる前に、すべてのアイテムが顧客の要件と業界標準に従って安全に梱包されていることを確認するための検査が行われます。

Lifepo4 バッテリーの利点
LiFePO4(リン酸鉄リチウム)電池は、近年ますます人気が高まっている充電式電池です。他の種類のリチウムイオン電池やリチウムポリマー電池に比べて多くの利点があります。 鉛蓄電池 ポータブル電子機器、電気自動車、エネルギー貯蔵装置などのさまざまな用途に適しています。
(1)高エネルギー密度
スタンフォード大学が2020年に実施した調査によると、リン酸鉄リチウム電池は、 エネルギー 従来の鉛蓄電池の密度。
(2)長寿
リン酸鉄リチウム電池の主な利点は 他の種類のリチウムイオン またはニッケル水素電池の長所は、サイクル寿命が長いため、寿命が長いことです。このため、長期間にわたって頻繁に放電/充電サイクルを行っても性能が著しく低下することが期待できる定置型電源システムでの使用に最適です。
(3)広い温度範囲
LiFePO4バッテリーは他のバッテリーよりも低温で動作する傾向がある。 バッテリーの化学特性、熱管理要件の低減、安全機能の向上。これにより、極端な温度により損傷が発生したり、バッテリー寿命が短くなる可能性がある場所でも安全に使用できます。.
(4)高い充放電効率
Lifepo4 電池 充電受け入れ性に優れ、深放電後でもすぐにフル充電状態に達することができ、アプリケーションによっては 1 時間以内に最大 95% まで充電できるため、ユーザーに優れた制御と利便性を提供します。
(5) 自己放電率が低い
自己放電率が低いため、 LiFePO4バッテリーは蓄えられたエネルギーを保持する 他のほとんどの化学物質よりも優れており、必要に応じて充電サイクルを延長できます。
Lifepo4バッテリーの欠点
LiFePO4電池 は、エネルギー密度が高く、安全特性に優れているため、さまざまな用途に適しています。ただし、使用するバッテリーの種類について十分な情報に基づいて決定する前に、考慮すべき欠点もいくつかあります。次の表に、これらの欠点をまとめます。
| アドバンテージ | 不利益 |
| 長いサイクル寿命 | 初期コストが高い |
| 低い自己放電率 | 温度感度 |
| 優れた安全性能 | 電力密度の低下 |
| 高エネルギー密度 | 充電容量の制限 |
初期費用 LiFePO4 バッテリーの寿命は、鉛蓄電池やニッケル水素電池などの他のタイプの充電式バッテリーよりも長く、化学反応や製造プロセスがより複雑なため長くなります。
さらに、その性能は極端な温度によって悪影響を受ける可能性があり、それが適用範囲を制限します。さらに、他のほとんどの化学物質と比較して比較的高いエネルギー密度を提供しますが、ニッケルベースの化学物質と比較すると電力密度(供給される電流量)は低下します。
最後に、長いサイクル寿命を持ちながら、 LiFePO4バッテリーは通常、充電が制限されています 容量。つまり、他の種類のバッテリーのように大量の充電をすぐに受け入れることはできません。
まとめると、他の技術に比べて多くの利点があるにもかかわらず、ユーザーは LiFePO4を選択する前にいくつかの要素を考慮する 特定の用途向けのセル。
これらには、利用可能な他の化学物質と比較した初期コスト、必要な充電容量、使用中に推奨動作範囲外の温度が発生するかどうかなどが含まれます。常にそうですが、適切なテクノロジーについて十分な情報に基づいて選択するには、特定のニーズを理解することが不可欠です。
Lifepo4バッテリーの用途
の LiFePO4電池の用途 数多くあります。民生用電子機器からエネルギー貯蔵システムまで、幅広い業界で使用されています。
前述の通り、 LiFePO4バッテリーはより高い比エネルギーと電力を提供します 安定性が高く、反応性が低いため、他のリチウムイオン化学よりも密度が高くなっています。さらに、優れた安全特性、長いサイクル寿命、高速充放電時間を備えています。
消費者分野では、 LiFePO4電池は、 ノートパソコン、携帯電話、電気自動車(EV)などのポータブル電子機器。
軽量であることから、EVでの使用には魅力的であり、車両全体の重量が軽減され、性能と燃費が向上します。同じ特性により、 太陽光発電での使用 あるいは、ピーク時に発電された余剰の再生可能電力を後で消費するために蓄えることができる風力発電バッテリーパックなどです。


LiFePO4 は、通信塔や信頼性の高い送電網接続にアクセスできないオフグリッド地域にバックアップ電源を供給するなどの産業用途にも使用されています。
さらに、これらのバッテリーは、必要に応じて緊急予備電力を供給することで、重要な瞬間に突然のシャットダウンを防ぐ無停電電源装置 (UPS) にも使用できます。これらの UPS システムは、停電や主電源の中断を引き起こすその他の災害など、極端な状況下でも貴重な情報を安全に保つ必要があるデータ センターでよく使用されます。
全体、 LiFePO4技術は最適な選択です 優れた安全基準、長いサイクル寿命、急速充電機能などの優れた機能により、さまざまなタイプのアプリケーションに適しています。
時間の経過による劣化を最小限に抑えながら大量のエネルギーを蓄える能力により、ユーザーは最も過酷な状況下でもデバイスに電力が供給され続けることを安心して知ることができます。
バッテリーの性能と寿命に影響を与える要因
Lifepo4 バッテリー 最高の性能と寿命を確保するには、さまざまな材料がそれぞれの特性に応じて慎重に選択されなければなりません。LiFePO4 セルの全体的な品質と信頼性は、次のようないくつかの要因によって決まります。
- 細胞化学組成
- 原材料の品質
- 製造条件
- 組み立て方法
- 動作環境
セルの化学組成は、セルのエネルギー密度、速度能力、および サイクル寿命一般的に、高品質の原材料を使用すると、低品質の原材料に比べてバッテリーの性能が大幅に向上します。
適切な製造条件も、セルが適切に機能することを保証する上で重要な役割を果たします。高温では電極部品が劣化する可能性があり、低温では電極と他の部品との接触が悪くなる可能性があります。
さらに、製造時に使用される組み立て方法はセルの電気的特性に影響を及ぼし、不適切な組み立て技術は容量の低下や寿命の短縮につながる可能性があります。
最後に、動作環境はバッテリーの長期にわたるパフォーマンスを決定します。極端な温度変化や湿気への曝露はバッテリーの寿命を縮める可能性があります。したがって、これらすべての要素は lifepo4バッテリーを選択する際に考慮する必要がある あらゆるアプリケーションに。
Lifepo4 バッテリーの保管要件
LiFePO4電池は、他のタイプの充電式電池に比べて優れていることから、ますます人気が高まっています。しかし、 適切な保管 これらの電池の適切な取り扱いは、電池の最適な性能と長寿命を確保するために重要です。以下に、電池を保管する際の重要な考慮事項を示します。 LiFePO4電池.
保存する上で最も重要な要素は LiFePO4バッテリーの効能は温度 制御。極端な温度は、バッテリー パックを構成するセルに回復不可能な損傷を与える可能性があります。たとえば、高温では低温よりもセル容量が急速に低下するため、適切に管理しないと早期故障につながる可能性があります。
したがって、これらのセルは 10 ~ 30 ℃ (50 ~ 86 ℉) の周囲温度で保管することをお勧めします。また、保管中に温度が大きく変動すると、セルの劣化が早まる可能性があるため、温度が大きく変動しないようにすることが重要です。

湿度も、 LiFePO4電池 セルはエネルギーを蓄え、寿命を維持します。セルは過度の湿気や結露から遠ざける必要があります。過度の湿気や結露はセル構造内部の腐食を引き起こし、時間の経過とともに全体的な容量を低下させる可能性があります。これは、相対湿度レベルを 70% 未満に維持することで実現できます。
さらに、セルは長期間保管する前に必ずしっかりと密封し、外気に触れないようにする必要があります。酸素に触れるとセル内の酸化プロセスが促進され、通常よりも大幅に早く性能が低下する可能性があります。
最大限の効率を確保するために LiFePO4バッテリーメーカーは、使用パターンや環境条件に応じて、保管中に通常 3 か月に 1 回程度、定期的に充電/放電サイクルを実行することを推奨しています。
さらに、各セルの寿命中は定期的に電圧レベルをチェックする必要があります。電圧低下は、接続のショートや個々のセルまたはパック自体のコンポーネントの故障など、より大きな問題を示している可能性があるためです。保管中および 通常のメンテナンス その後の試験結果によれば、LiFePO4 バッテリーは今後も長年にわたって信頼できる電源として機能し続けるでしょう。
Lifepo4バッテリーのリサイクル
リサイクル LiFePO4 バッテリーのリサイクルは、責任あるバッテリー使用の重要な部分です。リサイクルされた部品は新しいバッテリーの製造に使用でき、原材料の必要性を減らし、環境への影響を軽減するのに役立ちます。これらのバッテリーをリサイクルすることで、資源を節約し、地球環境を保護することができます。
リサイクルのプロセス LiFePO4セルはバッテリーの分解から始まります 部品に分解します。これには、個々のセル、セパレーター、端子、梱包材などをすべて収集することが含まれます。その後、それらは構成に基づいてさまざまなカテゴリに分類されます。
セルに含まれる金属は、プラスチックやゴム化合物などの他の材料とは別に抽出され、処理されます。回収された貴金属は、精錬工程でさらに処理され、純粋な金属インゴットが生成されます。一方、非金属は熱分解されて液体になり、成形プロセスの原料としてリサイクルされます。

この方法を使用すると、元の細胞塊の約 95% を何らかの方法で再利用できるため、焼却または埋め立てなどの従来のリサイクル方法に比べて非常に効率的です。
さらに、この技術は、現代の多くのリチウムイオン電池に使用されている希土類元素を採掘するために、未精製鉱床を採掘するよりも持続可能な選択肢を提供します。この技術は数十年にわたって開発されており、廃棄物管理や製品ライフサイクルに関する業界基準がますます厳しくなるにつれて進化し続けています。
リチウムイオン電池を扱う際の安全上の考慮事項
の LiFePO4電池の安全性 取り扱いの際は、これらの点を考慮する必要があります。LiFePO4 セルの製造元は、これらのセルの安全な使用、保管、廃棄に関する詳細なプロトコルを開発しています。LiFePO4 セルが寿命中に誤って取り扱われたり、不適切に保管されたり、安全に取り扱われなかったりしないようにするために、製造元のこのガイドラインに従うことが重要です。
| 潜在的な危険 | 緩和戦略 | 追加リソース |
|---|---|---|
| 火災の危険性 | 熱管理システム(TMS)を使用する | UL規格6800Bおよび1642C IEC62133 認証 UL 2054規格 定置型電源に使用される電池 アプリケーション |
| 過充電 | バッテリー監視システム(BMS)を活用する | IEEE 1547 規格 SAE J1772 チャージカプラインターフェース要件 |
| 短絡 | 適切に設計されたセルパックシステムを確保する | IPC/JEDEC JESD 95A 仕様 ISO 13485 品質管理システム |
製造元のガイドラインに従うことで、取り扱い、保管、廃棄に伴うリスクを軽減できます。 リチウムイオン電池 大幅。
さらに、設計、組み立て、テストのプロセスに関する追加要件を提供するいくつかの標準と品質管理システムが利用可能です。 バッテリーパックサプライヤー エンドユーザーも同様です。
- これらの標準には以下が含まれます。
- 熱管理システムに関する UL 規格 6800B および 1642C、充電式バッテリーに関する IEC/EN 62133。
- 定置型電力アプリケーションで使用されるバッテリーに関する UL 2054 規格。
- チャージカプラに関する IEEE 1547 規格。
- SAE J1772 チャージ カプラ インターフェイス要件。
- セルパック システム設計に関する IPC/JEDEC JESD 95A 仕様と、医療機器の設計および製造プロセスに関連する ISO 13485 品質管理システム。
これらの規格を遵守することで、長期にわたって LiFePO4 セルの適切な動作を保証しながら、潜在的な危険性を最小限に抑えることができます。
Lifepo4 バッテリー技術の今後の発展
の未来 LiFePO4バッテリー テクノロジーは、研究開発が盛んに行われている分野です。より大量のエネルギーを貯蔵し、サイクル寿命を延ばし、安全性を高め、コストを削減し、環境への影響を減らす能力は、いずれも近い将来に大きな進歩が見込まれる分野です。
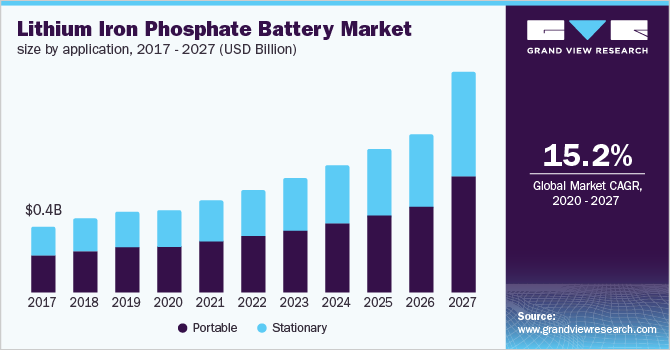
将来有望な進歩の道筋の 1 つはナノテクノロジーです。カーボンナノチューブやグラフェンなどのナノ材料を利用することで、現在の設計よりも電力密度が高く、比エネルギー貯蔵容量が高く、耐久性が向上したバッテリーを作成できる可能性があります。これにより、従来のリチウムイオン電池よりも速く充電でき、長持ちする軽量のポータブルバッテリーが実現する可能性があります。
改善の余地があるもう 1 つの分野は、新しい電解質の使用です。サイクル寿命をさらに向上させ、温度許容範囲も拡大できる新しい電解質配合が提案されています。さらに、現在商業生産で使用されている円筒形の代わりに、ポーチ セルや角柱セルなどの代替セル アーキテクチャを使用して材料コストを削減することを目指す新しい技術もいくつかあります。
これらの開発は、業界関係者と科学者の両方にとって刺激的な機会をもたらします。
- 電力密度と比エネルギー貯蔵能力の向上
- 新しい電解質配合によりサイクル寿命が向上
- 新しいセル構造による材料コストの潜在的な削減
- ナノ材料により充電時間が短縮
- より広い動作温度範囲と改良された安全機能の組み合わせ
これらの分野でどれだけの進歩が見られるかはまだ分からないが、一つ確かなことは、 LiFePO4電池 小型の民生用電子機器アプリケーションに加え、多くの大規模な固定式エネルギー貯蔵ニーズに対しても、実行可能なソリューションを提供し続けます。
結論
開発と LiFePO4電池の製造 市場に初めて登場して以来、長い道のりを歩んできました。これらの先進的なバッテリー システムはリチウムイオン技術の様相を変え、現在市場で入手可能な最も信頼性の高いバッテリー システムの 1 つと考えられています。
組み立て工程は非常に精密で、各セルは製造中に複数の段階を経て、最高品質の性能と安全基準を確保します。さらに、これらのセルは厳格な基準を満たす必要があります。 ストレージ要件 長期間にわたって効果を維持するためです。最後に、消耗または損傷したバッテリーのリサイクル プロセスにより、リソースが効率的かつ責任を持って再利用されることが保証されます。
結論は、 LiFePO4電池はエネルギー貯蔵における驚くべきマイルストーンである 信頼性、効率性、環境への配慮から、この技術は高く評価されています。
このタイプのバッテリー システムに適した新しい材料の研究が継続され、製造技術も向上しているため、電力密度、サイクル寿命、コスト削減、そしてさらに重要な点として、このような強力なデバイスを製造する際にメーカーが講じる安全対策のさらなる進歩が期待できます。
わずか数十年の間に私たちがどれだけ進歩したかは実に驚くべきことで、 LiFePO4バッテリーは優れた選択肢 信頼できるエネルギー貯蔵ソリューションをお探しの方へ。
