The Hazards and Countermeasures of Lithium Battery Overcharge

The safe and effective use of lithium batteries is essential in a large number of applications. The hazards associated with overcharged lithium batteries can be significant, including fire, explosions, and hazardous materials release. To prevent such risks it is important to understand the conditions that lead to lithium battery overcharge and take steps to prevent them from occurring. This article will discuss the potential hazards associated with an overcharged battery, as well as strategies for mitigating these risks.
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) cells are widely used due to their high energy density and relatively low weight compared to other types of rechargeable cell chemistries. However, if not properly managed they can become dangerously unstable when subjected to excessive charging current or voltage. Overcharging can cause irreversible damage known as thermal runaway which results in overheating and venting of toxic smoke or even fire or explosion risk. In addition, the released gases pose a health hazard if inhaled by personnel working in close proximity. As such, it is critical to have proper safety protocols in place to protect against these dangers.
What is The Lithium Battery Overcharge?
Refers to when the lithium battery is being charged, the charging voltage exceeds the set voltage, such as the rated voltage of the battery is 3.7V, and the fully charged voltage is 4.2±0.05V. That is, the maximum voltage is 4.25V, and it is called an overcharge if it exceeds 4.25V.
Lithium battery overcharge is like a ticking time bomb, ready to detonate and potentially cause catastrophic harm. It occurs when too much charge is applied to a lithium battery, resulting in an excessive build-up of energy that can cause the cells within it to rapidly heat up and even catch fire. This hazard presents a grave risk for anyone using or working with such batteries, as well as those who interact with them on a daily basis.
What Happens When a Lithium Battery is Overcharged?
When a lithium battery is overcharged, it can cause permanent damage to the cells of the battery. This type of damage will not be reversible by any means, and could potentially render the device unusable or even dangerous.
The hazards associated with overcharging lithium batteries include:
- Decrease in capacity due to reduced cell voltage.
- Increase in temperature which may cause thermal runaway leading to potential fire hazards.
- Degradation of electrolyte performance resulting in corrosion.
- Shortening of cycle life with fewer recharge cycles available.
How To Judge Whether The Lithium Battery Is Overcharged?
Judging whether a lithium battery is overcharged or not can be done in the following steps:
- Check the external temperature of the battery with your hand to feel if it is abnormally hot.
- Observe any smoke, sparks, odor, and other physical signs that are associated with an overcharge situation from the device containing the lithium battery.
- Monitor voltage readings on a multimeter for abnormal high voltages beyond what should be expected for a fully charged state for this specific type of lithium battery cell.
- If possible, monitor the current draw on a digital ammeter as well to determine potential short circuits occurring within the device itself due to excessive heating caused by an overcharged condition of the lithium battery cells being used in such applications.
If any one of these four conditions has been observed then immediate action must be taken to disconnect power sources and prevent further damage from occurring while attempting to find out what caused such an occurrence in the first place. It is important to remember that prevention is always better than cure when dealing with hazardous situations involving electrochemical energy storage devices like lithium batteries which could cause serious harm if mishandled or poorly maintained during their life cycle usage in an electronic system application setting.

How To Detect An Overcharged Battery
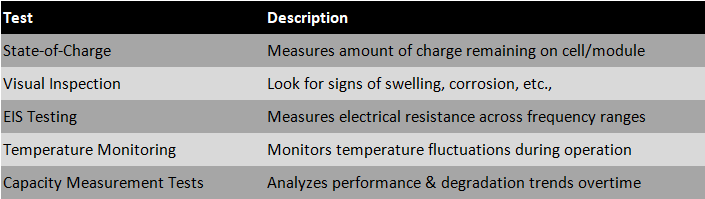
When discussing lithium battery overcharging, one of the most important considerations is how to detect an overcharged battery. This is a critical component in managing lithium batteries because if left undetected, an overcharge can cause thermal runaway and catastrophic failure. To assist with detection, there are various testing methods that can be employed by safety experts or technicians knowledgeable about lithium batteries.
The first step in detecting an overcharged battery is to examine its state of charge (SOC). A SOC test measures the amount of charge remaining on a cell or module and provides information regarding its current level of health. If the SOC falls outside acceptable parameters then further investigation should occur to identify potential causes such as excessive charging currents or voltages. Additionally, visual inspection for signs of swelling, corrosion, discoloration, or leakage should also be conducted.
Another way to detect an overcharged battery is through impedance measurements using specialized equipment like an Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy analyzer (EIS) which measure the electrical resistance across a range of frequencies. The results from this test provide insight into internal resistances within cells and modules as well as any capacity losses due to age or usage patterns. Data collected from these tests can indicate whether a battery has been exposed to high temperatures or extreme levels of discharge/overcharge cycles which could suggest an underlying problem with the system's control algorithm.
What are the Common Causes of Lithium Battery Overcharging?
(1) No Battery Protection System
Lithium battery overcharging can be caused by a variety of factors, but the most common is the lack of an adequate battery protection system. Without such a system in place, charging currents and voltages can exceed acceptable levels, leading to cell damage or fire hazard. Furthermore, if lithium batteries are exposed to high temperatures while being charged, they will be more vulnerable to thermal runaway events. As such, it is essential that all lithium-ion cells used in applications have appropriate protections installed.

These protections include temperature sensors for monitoring potentially hazardous heat build-up during charge cycles as well as voltage and current monitors which help ensure that maximum allowable levels are not exceeded. Additionally, modern safeguards often incorporate sophisticated algorithms which actively adjust charging parameters based on external conditions or specific usage scenarios. This helps prevent dangerous overcharge situations from occurring even when unexpected conditions arise. By ensuring these measures are implemented correctly, users can rest assured knowing their application is safe from potential risks associated with excessive charging rates.
(2) Improper Installation Of Battery Protection System
One of the most common causes of lithium battery overcharge is improper installation of a battery protection system. This can be likened to constructing a bridge without proper foundations, as it creates an unstable environment for charging and discharging that can result in serious damage or even catastrophic failure.
There are three key areas where errors made during installation can lead to dangerous levels of overcharge:
- Inadequate insulation between cells
- Insufficient voltage threshold settings on the board
- Failure to adequately test or adjust circuit parameters.
These mistakes all have one thing in common they create situations wherein too many current flows through the system, leading to thermal runaway and potentially hazardous conditions such as fire or explosion. To ensure safety when installing battery protection systems, manufacturers must take great care with each step of the process, from selecting components to ensuring correct operation before using them together in larger systems. Additionally, periodic testing should be done to make sure everything is working correctly and any necessary changes are implemented quickly and efficiently. By taking these precautions, lithium battery manufacturers can reduce their risk significantly while providing excellent performance and reliability for end consumers.
(3) Battery Protection System Failure

The failure of a battery protection system to prevent overcharging is a common cause of lithium battery overcharging. This occurs when the protection system does not properly detect, regulate, or control the charging current as it flows into the battery. Additionally, if the voltage levels exceed the recommended limits for safe operation, an excessive amount of energy can enter and damage the cells, potentially leading to catastrophic results.
The most effective way to mitigate such risks is by employing multiple layers of redundant safeguards throughout the design process. Designing with high-quality components that are robustly tested before use is essential in providing reliable performance. Furthermore, using intelligent safety monitoring systems helps maintain accurate status information about each cell’s temperature and voltage during charging cycles. Appropriate corrective actions should be taken immediately upon detection of any irregularities.
Lithium Battery BMS Can Prevent Overcharging
Recent research shows that in 2018, there were an estimated 1.3 million lithium batteries overcharged due to a lack of protective measures. This highlights the importance of using a Battery Management System (BMS) to protect against this hazard. A BMS is designed to monitor and regulate charging parameters such as temperature and current flow for each individual cell, ensuring safe operation and preventing overcharging.
There are three main advantages of utilizing a BMS:
- It extends battery life - by monitoring cell voltages and providing alerts if they become too low or high.
- Safety features - such as short-circuit protection help prevent accidents caused by improper wiring or mishandling of cells during installation.
- Cost savings - can be realized since having a BMS prevents costly repairs that may arise from overcharging or undercharging the battery pack.
When selecting a BMS, it is important to consider factors like cost, power rating, size, number of channels, communication protocol compatibility with other devices, and additional safety features such as thermal cutoffs and reverse polarity protection. By taking these into account when choosing a suitable system for your application you can ensure reliable performance while avoiding any potential risks associated with lithium battery overcharge hazards.
The 5 Measures to Prevent Overcharging
- The protection voltage is set in the BMS so that the protection voltage is lower than the peak voltage during overcharging.
- Improve the overcharge resistance of the battery through material modification (such as material coating).
- Add anti-overcharge additives, such as redox pairs, to the electrolyte.
- With the use of the voltage-sensitive membrane, when the battery is overcharged, the membrane resistance is significantly reduced, which acts as a shunt.
- The use of OSD and CID designs in square aluminum shell batteries is currently a general anti-overcharge design, while soft pack batteries cannot achieve similar desig

Can an Overcharged Lithium Battery be Repaired?
Generally speaking, an overcharged lithium battery cannot be repaired. However, it depends on the application and damage site of the lithium battery.
For a single battery
From the point of view of the positive electrode material alone, overshoot will cause changes in the material structure, and this change is irreversible, so the overcharged lithium battery cannot be repaired. In terms of the degree of damage, severe overcharging may cause an explosion, and slight overcharging will not cause thermal runaway, but will cause capacity decay.
For a battery pack
We can make certain repairs according to the damaged parts.
Some cells are damaged: Use a multimeter to measure the faulty cell and replace it with a cell of the same model and specification to ensure that all cells are in a healthy state and consistent (voltage, capacity, internal resistance and other errors are within a reasonable range).
The BMS damage: Test the response of the BMS to the current, and check whether the BMS is faulty, otherwise the entire BMS needs to be replaced to ensure that the BMS can normally detect and manage the battery pack.
What Is A Deep Discharge?

A deep discharge is a term used to describe the process of draining all stored energy from a lithium battery. This type of discharge can be dangerous because it subjects the cells in the battery to extreme stress and could cause permanent damage. It also causes significant increases in internal temperatures which, if left unchecked, could result in thermal runaway or fire.
To prevent this type of overcharge, lithium batteries should never be drained below their manufacturer-specified minimum voltage level - known as 'the cut-off point'. Battery Management Systems (BMS) are designed with various safeguards that limit discharging current and alert users when they approach this critical threshold. Additionally, regular monitoring of cell voltages by an experienced technician is essential for ensuring the safe operation of any high-powered system.
How to Charge Lithium Battery Correctly?
1. Suitable ambient temperature
Keeping lithium batteries at a suitable temperature is of the utmost importance as external temperatures can have a great effect on the battery’s performance.
If lithium batteries are exposed to high temperatures for prolonged periods, the battery capacity and charge quality will diminish.
In cold environments, lithium batteries require energy to regulate the internal temperature, something which consumes valuable power and isn't conducive to charging intervals.
For optimal operation, lithium batteries should be charged, discharged and operated within an ambient temperature range of 5°C-45°C.
2. Store the battery properly
Life lies in exercise. To maximize the efficiency of lithium-ion batteries, it is necessary to use them frequently to keep the electrons in the lithium-ion batteries in a state of flow.
If the lithium battery is not used frequently, please store the battery properly. Before storage, make sure that the battery power is kept at 30%-70%, in a cool, dry, and ventilated environment, and perform a charge-discharge cycle every 3-6 months.
3. A suitable charger
The charger needs to match the voltage with the voltage of the lithium battery, and the current with the ampere-hour capacity of the lithium battery. In addition, the charger has a charging protection function to prevent overcharging and failure.
A suitable lithium battery charger is to charge at a constant current first, and then when the battery voltage rises to 4.2V, the voltage will no longer rise, and the charger will detect the current, and if the current is less than a certain value, the charging will end.
4. Avoid full charge and discharge
Keeping lithium batteries properly charged and discharged can prolong battery life. Because many lithium batteries now have no memory effect, maintaining the battery power at 10%~90% is more conducive to protecting the battery.
When charging the batteries of digital products such as mobile phones and laptops, it is not necessary to reach the maximum value.
5. Avoiding fast charging
To increase the rate at which a battery can be charged, manufacturers either increase the amperage or change the voltage to increase potential energy, and this is what strains lithium cells and is a potential catalyst for damaging them.
Therefore, from the long-term use of the battery, fast charging affects the service life of the battery more than normal charging.

Summarize
Lithium battery overcharge is a serious issue that can cause permanent damage to the batteries, leading to loss of capacity and high impedance. To avoid these issues, it is important for users to understand how to charge lithium batteries correctly.
One example of proper charging procedures would be using a Battery Management System (BMS). A BMS will monitor the charge cycle and prevent overcharging by cutting off power if necessary. In addition, regular deep discharges are recommended in order to maintain the optimal performance of lithium batteries. Deep discharge cycles should not exceed 50-80% depth and should never reach 0%, as this could lead to cell reversal and other irreversible damage.
Overall, understanding the hazards associated with lithium battery overcharging and learning the correct charging techniques can help ensure safety while maximizing the life cycle of lithium batteries. By following best practices such as utilizing a BMS or deep discharging regularly, you can protect yourself from unnecessary risk while ensuring that your lithium batteries stay healthy for years to come.
Learn More Top Questions About Lithium Batteries!
