Lifepo4 Batteries and Winter Woes: Can LFP Batteries Freeze?

Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are an increasingly popular form of energy storage for many applications due to their lightweight and high-energy density. However, a key question that researchers have been asking is if LiFePO4 batteries can freeze in certain conditions. This article will review the current research available on this subject to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of this technology's capacity for freezing temperatures.
The impact of temperature on the performance of any battery type is significant, as it affects both its physical characteristics and chemical processes. Understanding how LiFePO4 cells react to cold environments allows us to better optimize their use in various settings. As such, we will explore what happens when these batteries experience low temperatures, including the potential risks associated with a frozen battery cell.
Finally, we will discuss possible solutions to prevent or mitigate any damage caused by freezing temperatures so users can continue using LiFePO4 cells safely while taking advantage of all their benefits under different environmental conditions.
By combining theoretical knowledge with practical considerations, readers should gain valuable insight into how they can ensure the optimal operation of lithium iron phosphate batteries regardless of external temperature conditions.
Definition Of Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that offers high energy density and long cycle life. They are widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, solar storage systems, and other applications where reliable power is needed.
LiFePO4 batteries have a unique chemical composition consisting of lithium-iron-phosphate molecules which provide excellent safety features compared to traditional lead acid or nickel metal hydride batteries. These features make them ideal for applications that require frequent charging or discharging cycles.

The capacity of LiFePO4 cells can range from 1Ah up to 300 Ah depending on the size and design of the cell. Higher capacities allow more energy to be stored in one single unit while lower capacities give larger numbers of cells but with less total energy available per unit weight or volume. The higher capacity cells also tend to have better performance when it comes to charge/discharge efficiency and lifespan.
In terms of safety, LiFePO4 batteries are known for their low flammability risk due to their chemical structure and thermal stability when exposed to extreme temperatures or overcharging conditions. Additionally, there is no need for special maintenance practices like those required by lead acid batteries such as using distilled water for topping off electrolyte levels. This makes them easier to install and maintain than some other types of rechargeable batteries.
As a result, they remain an attractive choice for many applications requiring reliable power sources with minimal effort on the part of end users.
Temperature Tolerance Of Lifepo4 Batteries
A case study of a LiFePo4 electric vehicle battery in Norway provides insight into the temperature tolerance of such batteries. The car was used during a cold winter, with temperatures dropping to -20°C (-4°F). During this time, there were no problems with the performance or reliability of the battery despite its low-temperature exposure. This indicates that LiFePo4 batteries can tolerate sub-zero climates and still maintain their capacity for energy storage.
When it comes to preventing freezing, however, special measures must be taken. It is important to ensure proper maintenance and insulation to protect against extreme cold conditions as these could cause irreparable damage to the cells within a LiFePo4 battery.
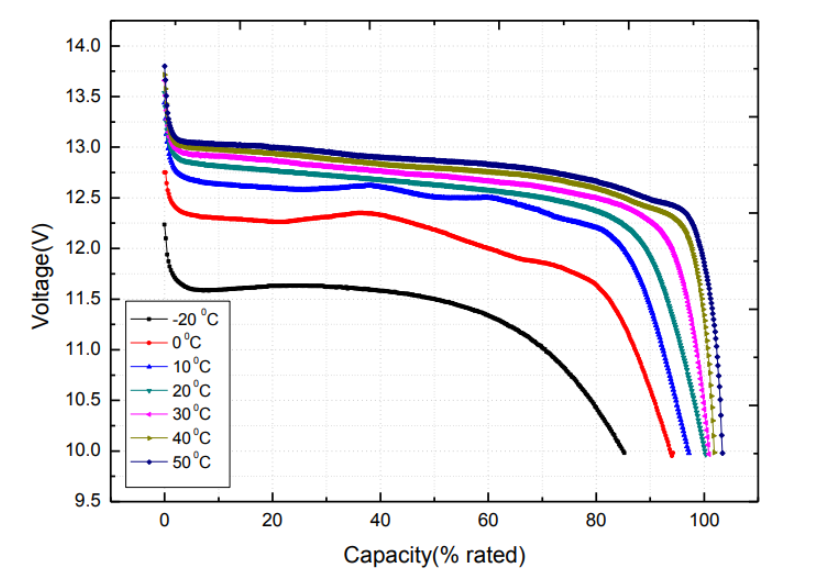
In addition, any charging should take place at room temperature in order to avoid an excessive drop in voltage due to the reduced conductivity caused by extremely cold environments. By taking appropriate precautions when using LiFePo4 batteries in cold climates, users can be assured of long-lasting performance and extended battery life.
In summary, while LiFePo4 batteries are capable of operating reliably in very low temperatures, additional steps need to be taken in order to protect them from freezing and preserve their lifespan under such conditions. With careful management and preventive measures adopted prior to use in cold climates, users can enjoy reliable operation without compromising on battery life expectancy.
Potential Damage From Freezing
Potential Damage From Freezing
When lifepo4 batteries freeze, there is potential for significant damage. Freezing may cause battery cells to swell and bulge, reduce performance capabilities, or even lead to permanent capacity loss. In extreme cases, the casing of a frozen battery can crack due to pressure changes caused by freezing temperatures. This can lead to corrosion and other serious harm that renders the battery fail.
In order to prevent such consequences from freezing lifepo4 batteries, it is important to take precautionary steps prior to exposing them to low temperatures. Battery enclosures should be properly sealed in order to inhibit moisture penetration and keep out cold air. And the charging system must be designed with temperature control mechanisms that regulate temperature during charge cycles and shut off when necessary.

Furthermore, if possible, avoid storing charged batteries in areas where they are likely exposed to below-freezing temperatures as this increases their susceptibility to failure from freezing conditions.
It is critical for those handling lifepo4 batteries to understand both how these cells behave at lower temperatures as well as proper methods for freeze prevention in order to maintain optimal functioning over time.
By taking preventive measures before exposure and understanding the risks associated with freezing conditions, users can maximize the lifespan of their lithium ion phosphate batteries while avoiding costly repairs or replacements down the line.
Storage Conditions For Lifepo4 Batteries
LiFePo4 batteries have become the go-to choice for energy storage due to their high energy density, long cycle life and low cost. However, it is important to consider the correct storage conditions for LiFePo4 batteries in order to ensure that they perform optimally.
When storing LiFePo4 batteries, it's essential to maintain a specific temperature range: 0°C - 45°C (32°F - 113°F). If stored outside of this temperature range, it can lead to significant damage or even complete failure of the battery. In particular, freezing temperatures can cause irreparable harm to the battery cells. The following should be kept in mind when considering LiFePo4 battery storage:
- Avoid extreme temperatures
- Store at an optimal charge level
- Use appropriate charging and discharging cycles
- Monitor overall performance regularly
- Keep away from direct sunlight and moisture
It is also advisable to use designated racks or cabinets specifically designed for lithium ion battery storage. These provide additional protection against external influences such as vibrations and impacts which may result in physical damage to the cells.

Furthermore, configurable shelves allow users to adjust the size and height of each shelf according to their needs while keeping them secure during transportation or handling procedures. This enables the safe stacking of multiple modules without any risk of short circuits caused by metal parts coming into contact with other components within the cabinet.
In summary, By taking these simple steps when storing LiFePo4 batteries, users will get the maximum performance out of their investment over time whilst minimizing risks associated with improper management tec.
Impact Of Low Temperatures On Battery Life
The impact of low temperatures on batteries is an important factor to consider when evaluating battery life. Low temperatures can significantly reduce the performance and voltage levels of LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) cells, making them less effective in cold weather applications. This section will examine how temperature affects battery life and explore methods for mitigating cold-weather degradation.
| Temperature Range | Performance Impact |
|---|---|
| 0 - 5°C | Minor decline |
| 5 - 10°C | Moderate decline |
| 10 - 15°C | Severe decline |
| Below 0°C | Shut down |
From the above table, it can be concluded that the effects of a cold environment are especially detrimental to LiFePO4 cells as they experience significant decreases in capacity and power output below 10 degrees Celsius (50 Degrees Fahrenheit).
At temperatures between 0-5 degrees Celsius (32-41 Degrees Fahrenheit), minor declines in performance may be observed but these should not affect the cell's overall lifespan or reliability.
When temperatures drop below zero degrees Celsius (32 Degrees Fahrenheit), LiFePO4 cells may shut down completely due to overvoltage protection mechanisms which limit their ability to deliver current under extreme conditions.

To mitigate the effects of cold weather, it’s recommended that users store their batteries at room temperature whenever possible and keep them out of direct sunlight during winter months. Additionally, if using LiFePO4 cells in colder climates, it is advisable to choose larger capacities than normal as this will help offset any losses in energy efficiency caused by lower temperatures.
In order to extend battery life even further, some manufacturers offer special thermal management systems designed specifically for use with LiFePO4 batteries in subzero environments. A well-managed system can ensure reliable performance even in the most hostile environmental conditions, allowing users to maximize their investment without compromising safety or longevity.
Charging In Cold Weather
Charging a Lifepo4 battery in cold weather can be like playing a game of chess; it requires careful planning and strategizing to make sure all the pieces are in place. In order for batteries to remain healthy, charging must take into account the environmental conditions. Below is an overview of three things you should consider when charging your Lithium Iron Phosphate (Lifepo4) battery in cold weather:
- Charging Speed: Cold temperatures reduce the rate at which a Lifepo4 battery charges, so adjusting your charger's settings accordingly is important. It may also help to turn on a heater nearby or use warm water to heat up the area around the battery while it charges.
- Careful Monitoring: Keeping an eye on temperature changes as well as voltage levels during charging is necessary to ensure that no damage occurs. Paying attention to any fluctuations helps prevent overcharging and other issues associated with using Lifepo4 batteries in cold temperatures.
- Maintenance: Performing regular maintenance on your Lifepo4 battery will help keep it running smoothly even when exposed to colder climates. Check for corrosion or dirt build-up, clean away debris from ports, and check connections regularly for signs of wear or tear.

When dealing with low temperatures, having knowledge about how best to charge a lifepo4 battery is key to keeping them functioning correctly. Taking actionable steps such as monitoring closely, maintaining regularly, and setting appropriate charging speed will provide users with peace of mind knowing their batteries have been properly cared for against harsh winter environments.
Discharging In Cold Weather
When discharging LiFePO4 batteries in cold weather, it is important to understand the impact of temperature on battery performance. The most significant factor affecting the discharge rate of a battery in cold temperatures is its internal resistance, which increases with decreasing temperature. This means that as the ambient temperature drops below 0°C, the available energy output from the battery decreases significantly.
As such, it is essential for users of LiFePO4 batteries to take into account both the ambient temperature and their own needs when considering how much power they require from their batteries during winter months.
Additionally, lithium ion cells have a lower operating voltage at low temperatures than at higher temperatures. When these cells are exposed to temperatures below 0°C or 32°F, an additional protection circuit must be used to prevent over-discharge and possible cell damage.

In addition, if LiFePO4 cells are discharged too deeply while in cold environments (below -20°C (-4°F)) they can freeze and become permanently damaged due to crystallization within the structure of the material itself. Therefore, proper monitoring and control should be taken when using LiFePO4 batteries in extremely cold conditions.
To ensure optimal performance of LiFePO4 batteries in cold weather conditions, all safety precautions should be taken when charging and discharging them according to manufacturers' guidelines. Furthermore, care should also be taken to choose cells suited for use in colder climates by selecting those with high Cold Temperature Performance (CTP) ratings which indicate better tolerance for freezing temperatures without compromising charge capacity or longevity.
By understanding the unique characteristics associated with using LiFePO4 technology in cold weather applications and taking necessary precautions for safe operation, users can ensure that maximum performance is achieved even during winter months.
Prevention Of Freezing
The effects of cold weather on LiFePO4 batteries are especially critical due to the potential for freezing. Freezing can cause damage that significantly shortens the battery's lifespan and affects its functionality. Therefore, the prevention of freezing is essential in order to ensure optimal performance and longevity of LiFePO4 batteries.

Temperature management is a key method when it comes to preventing freezing; this means keeping the internal temperature above 0°C by utilizing insulation materials or an interior heater.
Additionally, implementing a low-voltage cutoff design prevents deep discharge conditions which would render the battery unable to operate until recharged again. This also helps prevent overcharging, as using a charger with a built-in protection circuit will shut down if excessive current or voltage levels occur.
Finally, selecting high-quality cell components such as lithium iron phosphate cathode material increases energy density while providing better protection against extreme temperatures than other chemistry types like lead acid or nickel cadmium chemistries.
In order to maximize efficiency and effectiveness, strategies should be employed aimed at avoiding freezing situations and optimizing overall system performance through temperature management techniques, utilization of protective circuitry and selection of appropriate cell components offering improved cold weather protection capabilities.
Methods To Thaw Frozen Lifepo4 Batteries
Thawing frozen LiFePo4 batteries can be compared to thawing an icy winter landscape. To the uninitiated, it may seem like a daunting task; however, with proper technique and specific tools, the process can be relatively straightforward.
Safe thawing methods for LiFePo4 batteries involve gradually reintroducing heat into the battery cells from room temperature or slightly higher temperatures (according to manufacturer specifications). This should be done slowly over time to avoid any potential damage due to thermal shock.

A common method of doing this is by placing the cell in a warm water bath or using a specialized device such as a heated glove box that is designed specifically for thawing frozen batteries. Additionally, some manufacturers offer special heating pads that are designed to introduce controlled amounts of warmth into the cells without causing damage.
For cold weather conditions where the ambient temperature is below freezing, it is important to ensure that all exposed parts of the battery are covered with insulation material before attempting any sort of recharging procedure - even when using approved warming techniques. Doing this will help maintain consistent levels of the temperature inside the battery during charge cycles, thus minimizing any risk of further formation of ice crystals and prolonging its lifespan overall.
Ultimately, following these steps will help ensure a safe and successful thawing experience with no adverse effects on your LiFePo4 batteries.
Balancing Cells In Cold Weather
In order to protect LiFePo4 batteries from freezing, cell balancing(BMS) is an essential practice. Cell balancing ensures that all cells in a battery pack are within the same voltage range by equalizing each individual cell's charge and discharge rates.
This helps regulate temperatures during periods of cold weather and prevents any one cell from becoming too discharged or overcharged. Temperature regulation plays a key role in proper battery maintenance because it helps maintain optimal operating conditions for most lithium-ion batteries.
When using LiFePo4 batteries in low-temperature environments, it is important to properly balance the cells before attempting to recharge them since colder temperatures can cause prolonged charging times which may result in overcharging and eventual damage to the battery.

Additionally, if not balanced correctly, the rate at which energy flows through each cell will be unequal causing further issues with undercharging or overcharging. This makes regular monitoring of each cell’s voltage even more important as well as ensuring that no single cell becomes overly charged or discharged due to extreme temperature fluctuations.
Finally, when storing a LiFePo4 battery in cold climates, it is important to ensure that all components remain dry so moisture does not compromise their function or performance. Also, never expose these batteries directly to extremely low temperatures as this could lead to permanent damage such as freeze cracking and chemical changes which can render them useless.
With careful attention paid to temperature regulation and proper storage practices, LiFePo4 batteries can remain safe from harm caused by extreme climatic conditions like freezing.
Benefits Of Lifepo4 Batteries In Cold Climates
LiFePo4 batteries offer several advantages in cold climates. This technology offers excellent temperature stability and performance at low temperatures, making it an ideal choice for outdoor applications or operations in extremely cold climates. The following table outlines the key benefits of LiFePo4 batteries in cold conditions:
| Benefit | Description | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Performance | Excellent performance even in extremely low temperatures | Enables battery usage outdoors in winter without any significant drop-off in power output |
| Temperature Stability | High-temperature resistance ensures that cells don’t go into a thermal runaway | Provides a certain degree of safety while operating battery packs outdoors during colder months |
| Low-Temperature Operations | Impervious to overcharging or discharging at lower temperatures | Increases the lifespan of the battery by preventing permanent damage resulting from frozen cells |
Overall, LiFePo4 batteries provide superior usability and safety compared to other types of rechargeable batteries when used under cold conditions. With their high energy density, longer cycle life, and excellent temperature stability, they are well suited to long-term use in harsh environments such as industrial operations or remote locations with extreme weather fluctuations.
Furthermore, these batteries have been designed specifically for deep discharge cycles, allowing them greater capacity retention than traditional lead acid options.
Alternatives To Lifepo4 Batteries In Cold Climates
The choice is clear: if you want to remain powered in cold climates, find an alternative to LiFePo4 batteries. From lead-acid to nickel-metal-hydride and lithium-ion, sodium ion and flow batteries, there is a variety of solutions on the market that can help stay energized even during chilly conditions.
For those looking for reliability and longevity, lead-acid batteries are a tried and true option. Although some may overlook this type of battery due its weight and size, it boasts excellent performance at low temperatures with minimal self-discharge rates compared to other alternatives.

Nickel-metal-hydride (NiMH) also delivers great results in colder climates while offering higher energy density than lead acid; however, it comes at the expense of reduced cycle life when exposed to lower temperatures.
Additionally, newer technologies such as sodium ion or flow batteries offer increased charge capacities but still require further development before becoming widely available for commercial use.
No matter which solution you choose, proper maintenance will be key for achieving optimal performance under any condition, especially cold ones! It's vital to ensure your chosen battery is designed for wintery environments so you can maximize its effectiveness no matter what Mother Nature throws your way.
Proper Maintenance And Care For Lifepo4 Batteries
The alternatives to LiFePo4 batteries in cold climates have been discussed, but proper maintenance and care of these batteries is paramount. In order to extend the lifespan of a LiFePo4 battery, it must be properly maintained and taken care of when used in cold climates. As temperatures drop below freezing, there are several methods of temperature maintenance that can help ensure the optimal performance and life span of a LiFePo4 battery.
First off, proper storage should be practiced with LiFePo4 batteries when they will not be used for extended periods of time or during winter months. The environment where the battery is stored needs to remain at a consistently cool temperature, yet above-freezing levels. To achieve this goal, insulation such as bubble wrap or foam can be wrapped around the battery before putting into an insulated bag or container.

Furthermore, if possible, it is best to store them on concrete floors rather than wood surfaces because concrete holds less heat than wood does and thus keeps the surrounding area cooler. These measures work together to provide extra protection from any drops in temperature below freezing levels.
When handling and using a LiFePo4 battery out in the open air during cold weather conditions, another layer of protection may need to be applied depending on how low temperatures get. If necessary then insulating wraps can also protect against any direct contact between metal components and low-temperature exposure which could cause damage due to thermal shock or condensation build-up inside electronics housing causing short circuits and other malfunctions.
Additionally, some devices like electric vehicles might benefit from having heated garages so that their batteries don’t experience extreme cold while parked overnight or for longer periods of time unused.
In addition to physical protection measures mentioned above related to storage and usage, users should also pay attention to charging regimes specific for cold climate use cases since overcharging or undercharging a LiFePo4 battery at too high or low temperatures respectively can shorten its lifespan significantly whether by promoting electrophilic reactions due oxidation caused by excessive charge retention or degradation through crystallization processes occurring at unduly low voltages being applied continuously over long periods of time.

Monitoring Performance And Voltage Levels
Accurately monitoring the performance and voltage levels of LiFePO4 batteries is essential to ensure the optimal lifespan. Performance tracking can be done in a variety of ways, including measuring current, voltage and temperature over time. Battery voltage level indicators are also used for reporting on the state-of-charge (SOC) or internal resistance of the battery pack.
A number of methods exist to measure the overall health of a LiFePO4 battery such as cell balancing, which helps maintain an even charge throughout all cells within a battery pack; monitoring capacity loss from cycling; and assessing electrolyte specific gravity—allowing users to identify any changes that may indicate increased aging or degradation.
In addition to these measurements, there are specialized tools available for more detailed analysis. This includes advanced digital analyzers which provide data logging capabilities so that patterns can be identified quickly and early warning signs spotted before they become major problems down the line. Such tools are invaluable in ensuring good performance and extending the life expectancy of LiFePO4 batteries.

Troubleshooting Tips
When it comes to monitoring the performance and voltage levels of lifepo4 batteries, proper maintenance is key. However, in cold climates, the risk that a battery may freeze increases exponentially due to the drastic drop temperatures can have on its ability to hold a charge. Subsequently, this could lead to damage or complete failure if not monitored closely. The following troubleshooting tips should be taken into account when considering how best to care for your lifepo4 batteries during colder weather:
- Avoidance:
- Check the temperature rating of your battery before purchase so you know which conditions it is rated for.
- Store them at room temperature whenever possible by keeping them away from windows and other areas where cold air might infiltrate.
- Maintenance Care:
- Regularly check voltage levels with a voltmeter as extreme temperatures will reduce their capacity for energy storage.
- If the battery does freeze, heat slowly until it reaches an optimal level - never try and speed up this process as it could cause irreparable damage.
It's important to note that despite taking all these precautions there is always going to be a certain degree of risk involved when using any type of battery in colder climates. Therefore, regular monitoring and maintenance are essential in order to ensure that your device runs reliably throughout even the harshest winter months!

Conclusion
The use of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePo4) batteries in cold climates has proven to be a reliable and cost-effective solution for many applications. It is important, however, that the battery is properly cared for and stored in order to ensure its longevity. When storing LiFePo4 batteries at temperatures below freezing, it is essential to remember that they can experience damage from thermal shock or crystallization due to their low-temperature tolerance.
To avoid potential harm to the battery system, proper storage conditions must be followed when using LiFePo4 batteries in cold climates. This includes keeping them away from extreme temperatures, avoiding full discharges during long periods of non-use, and ensuring adequate ventilation while charging. Additionally, regular monitoring of performance and voltage levels should be conducted so any issues with the battery can be identified quickly before further damage occurs.
Overall, understanding how LiFePo4 batteries are affected by cold temperatures is crucial for proper maintenance and care. By following these guidelines and making appropriate adjustments based on environmental factors such as temperature, users can maximize the lifespan of their LiFePo4 batteries even under harsh winter conditions.
